Hi Folks,
Today I am going to tell you about what exactly SOLID Principles concepts are in simple terms.
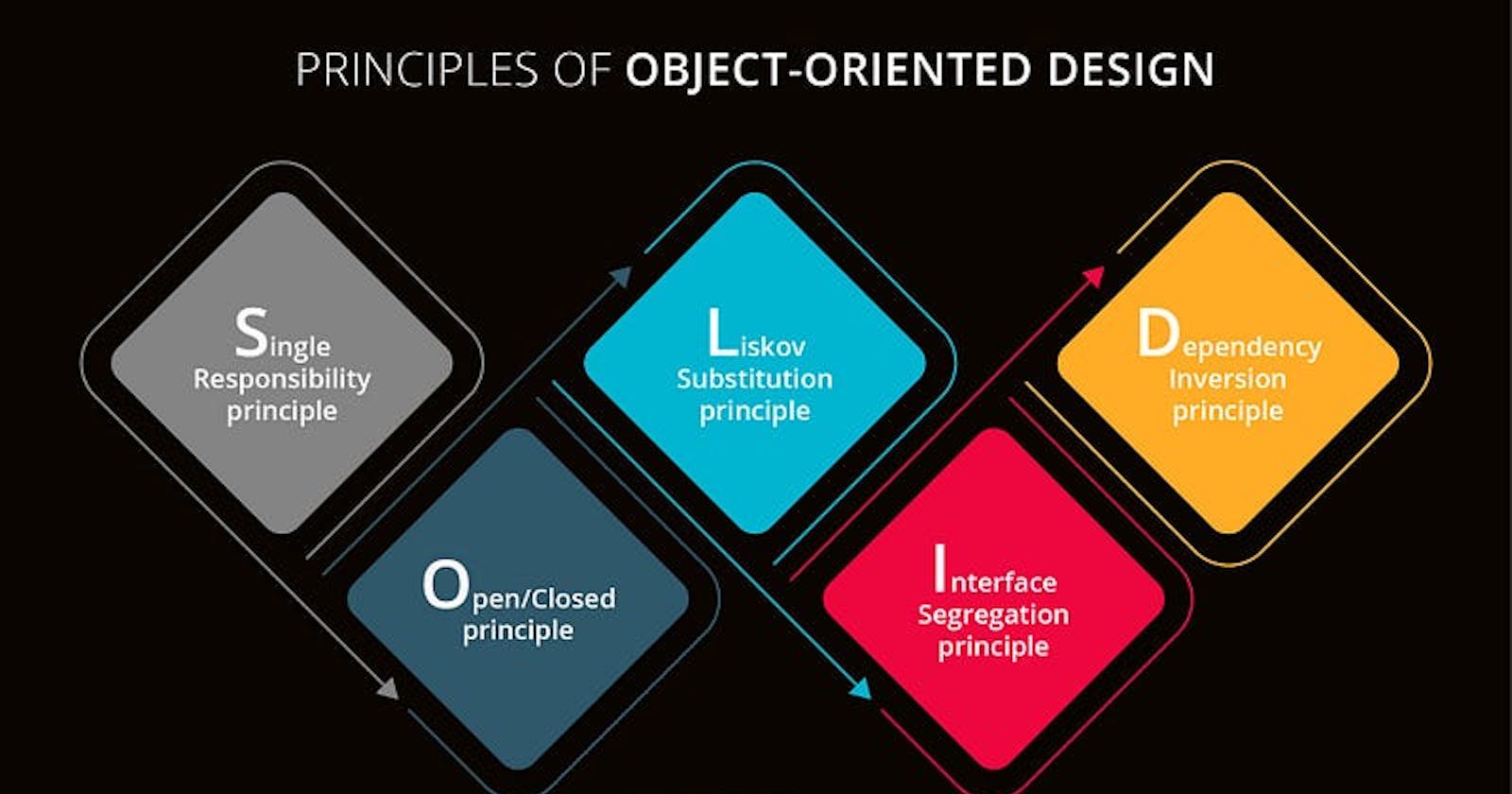
SOLID stands for
Image taken from google images.
1. Single responsibility principle
- Each class should have only one reason to change.
- Decouple unrelated functionalities and segregate them into standalone classes.
- Readability, reusability, and maintainability.
2. Open-closed principle
- Introduce abstractions in front of code that will change.
- Use only when requirements are reasonably predictable.
- Isolate your code from requirements change.
3. Liskov substitution principle
- Importance of proper sub-typing in inheritance hierarchies
- Seven rules.
1. Contravariance of arguments
2. Contravariance of result.
3. Pre Conditions .
4. Post Conditions
5. Exception rule.
6. In-variant rule.
7. Constraint rule.
- Especially important for code that will be consumed by others.
- SubTypes can be safely used instead of their supertypes.
4. Interface segregation principle
- Clients should only depend on the functionality they actually use.
- Principle of least knowledge and minimal coupling.
- Robust design, protection from design mistakes, better readability.
5. Dependency inversion principle
- Governs usage of abstractions
- Abstractions invert source code dependencies.
- Protection from change, reusability, breaking dependencies on external modules.
Thanks for reading and please share and subscribe for more information.